From Seed to Products: How Cannabis is Made
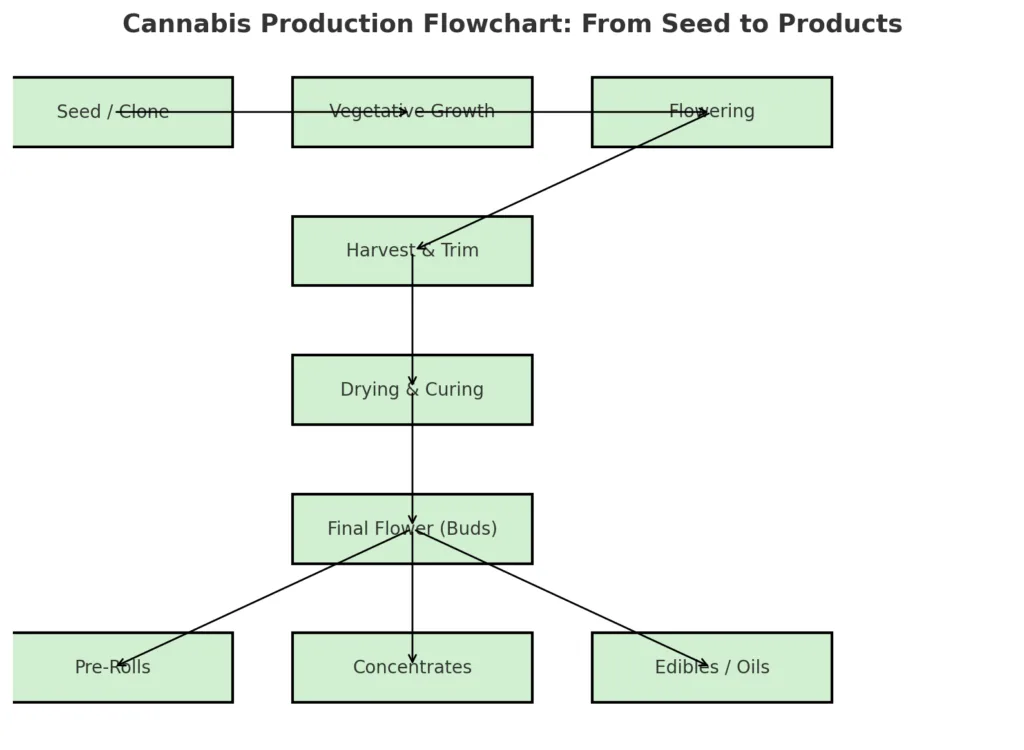
Growing the Plant
-
Seed or Clone Selection
-
The process begins with high-quality seeds or clones of the chosen strain
-
Breeders select strains for potency, terpene profile (aroma/flavor), and growth traits.
-
-
Vegetative Stage
-
Plants are grown under strong light (indoors or outdoors).
-
They receive nutrients rich in nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus.
-
This stage focuses on creating healthy leaves and stems.
-
-
Flowering Stage
-
Light cycles are switched to 12 hours of light / 12 hours of darkness (indoors) or naturally triggered outdoors.
-
Plants begin to develop buds (the part we consume).
-
Nutrients are adjusted to favor bloom development, usually with higher phosphorus and potassium.
-
Harvesting
-
Timing
-
Harvest happens when trichomes (tiny crystals on the buds) change from clear → cloudy → amber, signaling peak potency.
-
THC and terpene content are maximized at this stage.
-
-
Cutting & Trimming
-
Plants are cut down and the fan leaves removed.
-
Buds are carefully trimmed to remove sugar leaves while keeping the resin-rich trichomes intact.
-
This step makes buds look neat and improves flavor when smoked or vaped.
-
Drying & Curing
-
Drying
-
Buds are hung or placed on racks in a controlled room (temperature ~60–70°F, humidity ~50%).
-
This reduces moisture slowly, preventing mold while preserving cannabinoids and terpenes.
-
Takes about 7–14 days.
-
-
Curing
-
Once dry, buds are placed in airtight containers (like glass jars).
-
They’re “burped” (opened briefly) daily for a few weeks to release gases and moisture.
-
This enhances flavor, aroma, and smoothness of the smoke.
-
Packaging
-
After curing, buds are weighed (3.5g in your jar = an “eighth”).
-
They’re sealed in containers with proper labeling: strain name, THC %, CBD %, and lab testing info.
-
Packaging is child-resistant and often includes freshness seals.
Key Factors That Affect Quality
-
Genetics → determines potency, aroma, effects.
-
Cultivation method (indoor, outdoor, greenhouse).
-
Nutrient program & growing medium (soil, hydroponics, coco).
-
Harvest timing → too early = less potent, too late = degraded cannabinoids.
-
Curing quality → the difference between harsh weed and smooth, flavorful buds.
From Flower to Products
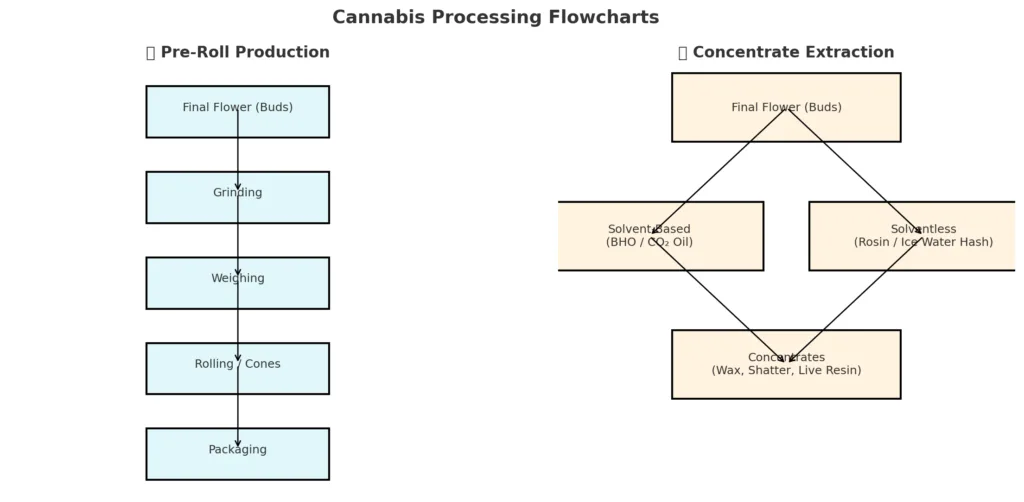
1. Pre-Rolls (Joints & Blunts)
Pre-rolls are simply ground cannabis flower rolled into cones or blunt wraps.
Step-by-step:
-
Grinding → The dried buds are ground into uniform, fluffy pieces.
-
Weighing → Exact amounts (0.5g, 1g, etc.) are measured for consistency.
-
Rolling → The flower is machine-rolled or hand-rolled into paper cones. Some include filters/tips for smoother smoking.
-
Packaging → Finished pre-rolls are sealed in tubes or multi-packs to stay fresh.
Sometimes producers add kief, hash, or concentrate oil to make “infused pre-rolls” (stronger, more flavorful).
2. Concentrates
Concentrates are made by extracting cannabinoids (THC, CBD) and terpenes from the flower. They come in many forms — wax, shatter, rosin, live resin, oils, etc.
Solvent-Based Extraction
-
Butane Hash Oil (BHO) → Butane is run through the cannabis, pulling out cannabinoids/terpenes. Then, the solvent is purged with heat/vacuum, leaving sticky wax/shatter.
-
CO₂ Oil → CO₂ gas under pressure extracts cannabinoids. This is common for vape cartridges.
Solventless Extraction
-
Rosin → Flower or hash is pressed with heat & pressure, squeezing out sticky resin.
-
Ice Water Hash (Bubble Hash) → Buds are agitated in ice water; trichomes break off and are filtered, then dried.
The type of concentrate depends on temperature, pressure, and processing method.
3. Edibles & Infusions
Flower can also be turned into edibles by first making cannabis-infused oils or butter.
-
Decarboxylation → Buds are gently heated (~240°F) to activate THC.
-
Infusion → Cannabis is simmered in butter, coconut oil, or MCT oil to absorb cannabinoids.
-
Cooking → The infused oil is then used to make gummies, chocolates, drinks, baked goods, etc.
4. Tinctures & Oils
-
Cannabis flower is extracted into alcohol or MCT oil.
-
This creates a liquid form that can be taken under the tongue (sublingually) for quick absorption.
Why Different Products Exist
-
Flower = traditional, smoking/vaping, balanced effects.
-
Pre-Rolls = convenient, no grinding/rolling needed.
-
Concentrates = much stronger, for experienced users.
-
Edibles = long-lasting effects, discreet.
-
Tinctures/Oils = controlled dosing, medical use.